Chameleon cross development
The unofficial page
by Avelino Herrera



The Chameleon is a powerful 24 bit programable audio DSP engine. It is manufactured by Soundart and can load a great variety of applications such as analog modelling polysynths, phat monosynths, filter banks, effect processors, et cétera. The Chameleon contains a powerful Coldfire processor plus a Motorola DSP 56303 and the user can build his own applications (or "skins") ussing the software development kit freely available at Soundart site.
The Chameleon SDK is distributed only in binary form for Win32 architectures. This page appears as an effort to create a development toolchain for a non-Win32 architecture like Linux. I want to thank Soundart for all the support and for answer all my technical e-mails and forum questions :-).
Here are the steps to build the GNU toolchain for ColdFire. All operations as root.
I have created a chameleon folder at my /mnt/scratch second hard disk. This folder will be called PREFIX henceforth (so, in my computer PREFIX=/mnt/scratch/chameleon).
binutilsI have compiled binutils 2.15. Download it here.
mkdir PREFIX/binutils-build
cd PREFIX/binutils-build
BINUTILS_SOURCE/configure --prefix=PREFIX --target=m68k-elf
make
make install
export PATH=$PATH:PREFIX/bin
BINUTILS_SOURCE is the folder where binutils is unpacked. Note the export shell command: this is for further use by the compiler.
include and lib folders from Chameleon SDK Windows installation folderRemember to mount your Windows partition :-)
mkdir PREFIX/sdk
cp -r /mnt/win/Program\ Files/Chameleon.sdk/include PREFIX/sdk
cp -r /mnt/win/Program\ Files/Chameleon.sdk/lib PREFIX/sdk
gcc-lib folder from bin/coldfire/lib folder at Chameleon SDK Windows folder
cp -r /mnt/win/Program\ Files/Chameleon.sdk/bin/coldfire/lib/gcc-lib PREFIX/sdk
gcc 2.95.2Use the 2.95.2 version because this is the version that uses the Windows SDK. Download it here.
mkdir PREFIX/gcc-build
cd PREFIX/gcc-build
cp PREFIX/sdk/gcc-lib/m68k-elf/2.95.2/m5200/mhwdiv/libgcc.a .
GCC_SOURCE/configure --prefix=PREFIX --target=m68k-elf --with-headers=PREFIX/sdk/gcc-lib/m68k-elf/2.95.2/include --disable-multilib --with-newlib --enable-languages="c"
make
make install
Note the 3rd line: "cp PREFIX/sdk/gcc-lib/m68k-elf/2.95.2/m5200/mhwdiv/libgcc.a .". We need to copy the libgcc.a to the gcc-build folder. libgcc.a is a library of internal subroutines that GCC uses to overcome shortcomings of particular machines, or special needs for some languages. In this case: Coldfire and C language. Note that there is no C++ support.
Let's write a simple Makefile and a very simple test source code:
PREFIX=/mnt/scratch/chameleon
LIBPATH=${PREFIX}/sdk/lib/model01/release
CC=m68k-elf-gcc
OBJCOPY=m68k-elf-objcopy
CFLAGS=-m5200 -msoft-float -malign-int -Wall -fno-hosted -fno-builtin -s -D__mc68000__ -D__BIG_ENDIAN__ -D__m68k__ -D__rtems__ -D__mot68 -DCHAMELEON_MODEL=01 -I ${PREFIX}/sdk/include/chameleon -I ${PREFIX}/sdk/include/rtems -I ${PREFIX}/sdk/include/midishare -I ${PREFIX}/sdk/include/newlib
PROJECT=test
LDFLAGS=-nostdlib -Wl,--cref -Wl,-Map,${PROJECT}.map -Wl,-T${PREFIX}/sdk/lib/model01.ld -Wl,-u,start -m5200 -mmac -mhwdiv -nostartfiles -Wl,-n -Wl,--start-group ${PROJECT}.o ${PREFIX}/sdk/lib/model01/release/chameleon.a ${PREFIX}/sdk/lib/model01/release/rtems.a ${PREFIX}/sdk/lib/model01/release/rtems_libcsupport.a ${PREFIX}/sdk/lib/model01/release/midishare.a ${PREFIX}/sdk/lib/model01/release/libc.a ${PREFIX}/sdk/lib/model01/release/libm.a -lgcc
linking: compiling
${CC} -o ${PROJECT}.elf ${LDFLAGS}
dependencies: ${PROJECT}.c
${CC} -M -MG ${CFLAGS} ${PROJECT}.c | sed 's@^\(.*\)\.o:@${PROJECT}/\1.d ${PROJECT}/\1.o:@' > ${PROJECT}.d
compiling: ${PROJECT}.c
${CC} ${CFLAGS} ${PROJECT}.c -c -o ${PROJECT}.o
clean:
rm -f *~ *.o *.map *.elf
Note that the PREFIX value is probably valid only for me ;-). The test source code is:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <rtems.h>
#include <chameleon.h>
#define WORKSPACE_SIZE 128*1024
rtems_unsigned32 rtems_workspace_size = WORKSPACE_SIZE;
rtems_unsigned32 rtems_workspace_start[WORKSPACE_SIZE];
rtems_task rtems_main(rtems_task_argument ignored)
{
int panel;
/* TRACE("Hello World\n"); */
panel = panel_init();
if (panel)
{
panel_out_lcd_print(panel, 0, 0, "HELLO WORLD ");
panel_out_lcd_print(panel, 1, 0, " from Linux :-)");
}
rtems_task_delete(RTEMS_SELF);
}
Both files can be cleanly downloaded here and here. The Makefile has been written with a lot of help from Soundart and the test code is an adaptation on the main.c published by Soundart as a SDK example code (thanks again, folks :-)).
Now, execute the make command and if it is allright you should have a file named test.elf in your current folder. Here is the ELF file generated by me.
We have to convert the test.elf file generated by linker to a MIDI file that we can send throw MIDI cable to the Chameleon. This is the main handicap of the toolchain because Soundart uses a propietary and non-free format to convert the ELF file to SysEx data into a MIDI file.
Fortunately the toolkit.exe application can be executed by wine and only requires the mfc42.dll and mfc42loc.dll dynamic libraries to run ok.
Here are some screenshots of the toolkit.exe running on my Linux box.
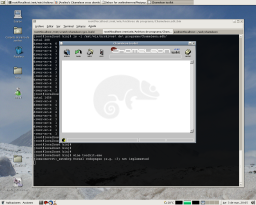
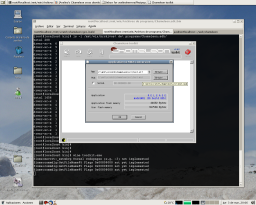
The toolkit.exe application generates a MIDI file that we can now send :-). Here is the file I have generated.
We can use any sequencer to send the MIDI file to the Chameleon. I have used the pmidi application that uses a very simple command line parameters interface.
With pmidi -l it shows me the available MIDI ports. On my computer:
Port Client name Port name 64:0 ES1371 ES1371
Turn on the Chameleon while pressing the shift key, connect the computer MIDI Out the the Chameleon MIDI In and type the command:
pmidi -p 64:0 test.mid
Use your MIDI port number pair and your MIDI file name to send the MIDI file throw the hardware MIDI port.
Wow!! :-) That's great. Your first Chameleon application built on Linux ;-).
The DSP 56303 toolchain is a bit complicated to build because the GNU Compiler Collection does not support it :-(. The most approximated way to build this toolchain is to use the old Motorola's dsp56k-gcc: a modification of the GCC 1.37.1 for the DSP 56000 models. The original package can be obtained here and it must be modified to build it with actual versions of GCC. Here are the steps to patch the dsp56k-gcc source package:
Makefile: Set the "prefix" variable to a desired value (it is empty by default).Makefile: Set the "INSTALLDIR" variable to a desired value (it is empty by default). Here is where gcc executables will be moved.gcc.c: Add "#include <errno.h>" at the top of file and comment the following lines
extern int errno, sys_nerr; extern char *sys_errlist[];at "pfatal_with_name", "perror_with_name" and "perror_exec" functions.
tree.c, expr.c and emit-rtl.c: Replace '#include "gvarargs.h"' by '#include <stdarg.h>'.cccp.c: Comment the "struct tm *localtime ();" line at "special_symbol" function and insert "#include <time.h>" at top of file.cccp.c: Comment the following lines
#if ! defined( _INTELC32_ ) && ! defined( __WATCOMC__ ) extern int errno; #endif #if ! defined( __WATCOMC__ ) extern int sys_nerr; #endif extern char *sys_errlist[];at functions "error_from_errno" and "perror_with_name", and add "#include <errno.h>" at top of file.
cccp.c: Insert "#include <string.h>" and comment the "bzero", "bcopy" and "bcmp" function definitions.cccp.c: Comment the "extern char *malloc ();" line at "xmalloc".cccp.c: Comment the "extern char *realloc ();" line at "xrealloc".cccp.c: Comment the "extern char *malloc ();" line at "xcalloc".gcc.c: Change the STANDARD_EXEC_PREFIX constant to a correct value (INSTALLDIR at Makefile).Now at INSTALLDIR folder we have the executable files g56k, g56-cc1 and mcpp. Now we have to put the asm56000 and the dsplnk executables in the PATH because they are invoked by the compiler, but these executable files are not part of dsp56k-gcc and are not ported to Linux neither open source :-(.
I found an initial solution to this problem: I used the asm56000.exe and dsplnk.exe MS-DOS executables and created two shell scripts named asm56000 and dsplnk that executes both MS-DOS executables into dosbox. Here are that executable files and some other stuff:
dosbox.conf: An alternate dosbox configuration file. You must adjust the "mount" line at "autoexec" section to your INSTALLDIR. Place this file wherever you want :-)asm56000 asm56000.bat asm56000.exe dsplnk dsplnk.bat dsplnk.exe dos4wg.exe mountd.bat dsp56k-gccat INSTALLDIR. Change the DOSBOXCONF value in
asm56000 and dsplnk scripts to the full path of the dosbox.conf file.crt0563l.cln crt0563x.cln crt0563y.cln lib563cl.clb lib563cx.clb lib563cy.clbfrom Chameleon SDK ./bin/dsp56303/lib subfolder to a folder you want (this will be the DSPLIB folder).
dsl56k-gcc script to your value.Now, let's make a test compilation :-). Download o write a trivial C program and compile it with the dsp56k-gcc script:
$ dsp56k-gcc -o hola.cld hola.c
Wow! that's great! ^_^ Now we have a .CLD file in current folder :-). Note that the resulting files from compilation (object code and linked code) are uppercase named. This happens because the assembling and the linking processes runs under a dos emulator.
NOTE: The Chameleon SDK comes with the asm56300.exe and dsplnk.exe DSP563xx related tools, but they cannot be run in DOS mode. I think the dosemu package can emulate a windows console and, perhaps, we could execute these tools instead of the 56000 ones (I have to test :-).
There are many thigs to do :-)
dsp56k-gcc.Special thanks:
Here is my e-mail address. Feel free to send me any sugestions/corrections about this page.
